React 里的最小堆

React 里的最小堆
React 目前使用的是 flow 做类型标注,为了方便阅读和执行,我将其转换成立 ts 的实现,逻辑方面并没有做任何修改。
type Heap<T extends Item> = Array<T>;
type Item = {
id: number,
sortIndex: number,
};
function push<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>, node: T) {
const index = heap.length;
heap.push(node);
shiftUp(heap, node, index);
}
function peek<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>): T | null {
return heap.length === 0 ? null : heap[0];
}
function pop<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>): T | null {
if (heap.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const first = heap[0];
const last = heap.pop();
if (last !== first) {
heap[0] = last;
shiftDown(heap, last, 0);
}
return first;
}
function shiftUp<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>, node: T, i: number) {
let index = i;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >>> 1;
const parent = heap[parentIndex];
if (compare(parent, node) > 0) {
heap[parentIndex] = node;
heap[index] = parent;
index = parentIndex;
} else {
return;
}
}
}
function shiftDown<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>, node: T, i: number) {
let index = i;
const length = heap.length;
const halfLength = length >>> 1;
while (index < halfLength) {
const leftIndex = (index + 1) * 2 - 1;
const left = heap[leftIndex];
const rightIndex = leftIndex + 1;
const right = heap[rightIndex];
if (compare(left, node) < 0) {
if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, left) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
heap[index] = left;
heap[leftIndex] = node;
index = leftIndex;
}
} else if (rightIndex < length && compare(right, node) < 0) {
heap[index] = right;
heap[rightIndex] = node;
index = rightIndex;
} else {
return
}
}
}
function compare(a: Item, b: Item) {
const diff = a.sortIndex - b.sortIndex;
return diff !== 0 ? diff : a.id - b.id;
}
// 测试数据
const queue: Heap<Item> = [];
push(queue, { sortIndex: 10, id: 1 });
push(queue, { sortIndex: 3, id: 2 });
console.log(queue); // [2, 1]
push(queue, { sortIndex: 11, id: 3 });
console.log(queue); // [2, 1, 3]
push(queue, { sortIndex: 8, id: 4 });
console.log(queue); // [2, 4, 3, 1]通过 compare 函数,我们知道,在比较两个元素优先级时,使用的是 sortIndex, 相同情况下再比较 id,本次我们只关心最小堆的实现,我们只需要知道比较函数用来确认优先级即可,我们完全可以自定义这个比较函数。
其他的方法,我们先了解一下堆的性质后在讨论。
堆的一些性质
Heap,即堆,在存储上是一个数组,逻辑上是一颗二叉树,且这颗二叉树在任何阶段都需要满足它是完全二叉树,即元素是从上至下,从左到右,在中间是不能有缺失的。
还有一点是根据堆是最小堆还是最大堆,每一个节点的值都必须大于等于或者小于等于其孩子节点的值,如下图所示:
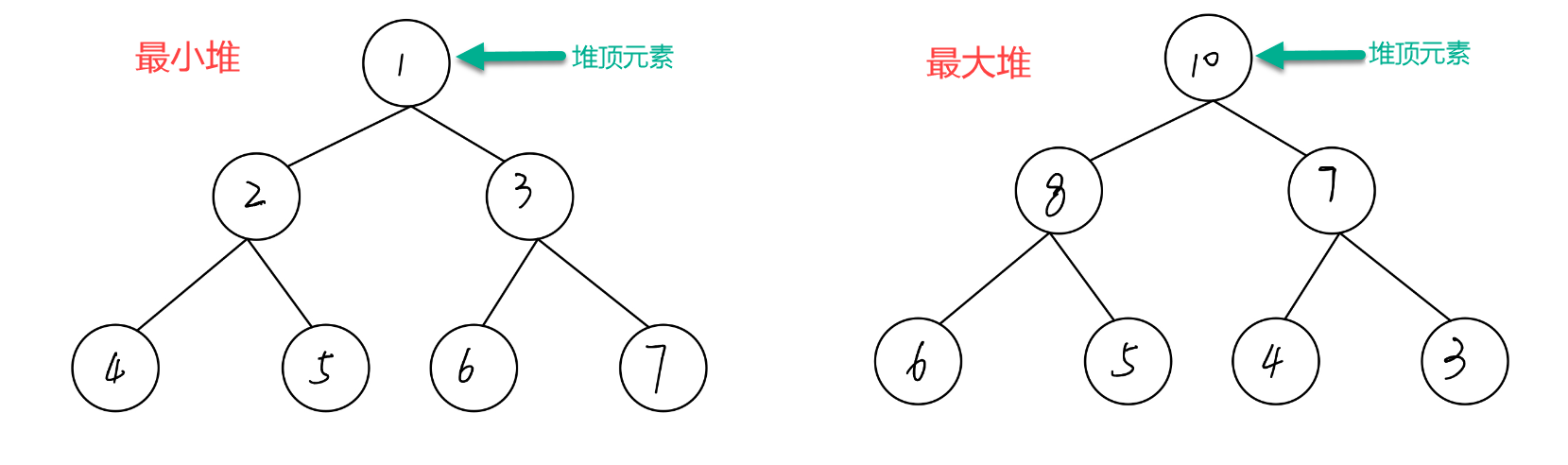
那么,二叉树存储成数组,怎么查询子节和父节点呢?
其实这个父子关系可以和数组的索引有关系。我们不妨以上图的最小堆作为例子,它的节点的值刚好是连续的从 1 至 7,我们就先把它当成索引。
以节点 3 为例子,它的左孩子节点为 6,即 3 * 2;它的右孩子节点为 7,即 6 + 1;
节点 5 的父节点为 2,即 5 / 2 的整数部分;节点 4 的父节点同样为 2。
我们还能发现总计 7 个元素,4-7 这些节点没有孩子节点,即,大于 7 / 2 的整数部分的元素没有孩子节点。我们不妨想象一下,如果存在第 8 号元素,该结论也成立。
需要注意的是,编程领域里索引是从 0 开始的,我们当前可以让数组里的第 0 个位置不存放元素,但是 React 的实现里并没有这么做,所以我们在做相关操作时,需要考虑这个位置。
还有一点是如何构建初始的堆?React 的实现里没有也不需要,因为我们完全可以从一个空堆开始,循环将元素插入即可,虽然这样效率比较低 O(N * logN)(因为堆的插入删除是 O(logN)),但是比较简单。我们只需要知道,真正的建堆操作可以达到 O(N) 的时间复杂度。
查看堆顶元素
这是堆最简单的操纵,如果存在堆顶元素返回即可。
function peek<T extends Item>(heap: Heap<T>): T | null {
return heap.length === 0 ? null : heap[0];
}取出堆顶元素
取出堆定元素,由与需要移除,这个位置的空缺我们会让最后一个元素移除后补位,这就可能破坏堆的性质(每一个节点的值都必须大于等于或者小于等于其孩子节点的值)。
所以我们还需要执行 shiftDown 来维护堆。shiftDown 会从堆顶开始,将堆顶元素与两颗子树的较小的那个进行交换,之后对进行交换的那个位置的子树循环地执行此操作,直到最后交换到叶子节点。
我们已经知道了如何通过索引查找两个子节点,以及存不存在子节点。
插入元素
直接在堆的末尾插入元素,此时,堆同样有可能不满足我们此前提到的性质。
我们需要一个类似的 shiftUp 操作来维护堆,shiftUp 相对 shiftDown, 简单一些,一个节点的父节点最多只有一个,最坏的情况下,我们需要不断循环,直到这个节点成为堆顶元素(没有父节点)。
我们也知道了如何通过索引查找父节点。
总结
比起每次插入后,执行排序来确认优先级,堆的操作更为高效。
工作生活上,我们也要学会给事情排上优先级。
最小堆是 React 里调度模块里的重要一环,如果我们要学习 React,需要掌握此算法。